How to write and develop Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
KPIs aren't a one and done, they take a deep understanding to define and must be developed over time.

KPIs aren't a one and done, they take a deep understanding to define and must be developed over time.
SubscribeWhat is a Key Performance Indicator (KPI)?KPIs, or Key Performance Indicators, are strategic objectives that companies or individuals set to focus on a target and stay on track.
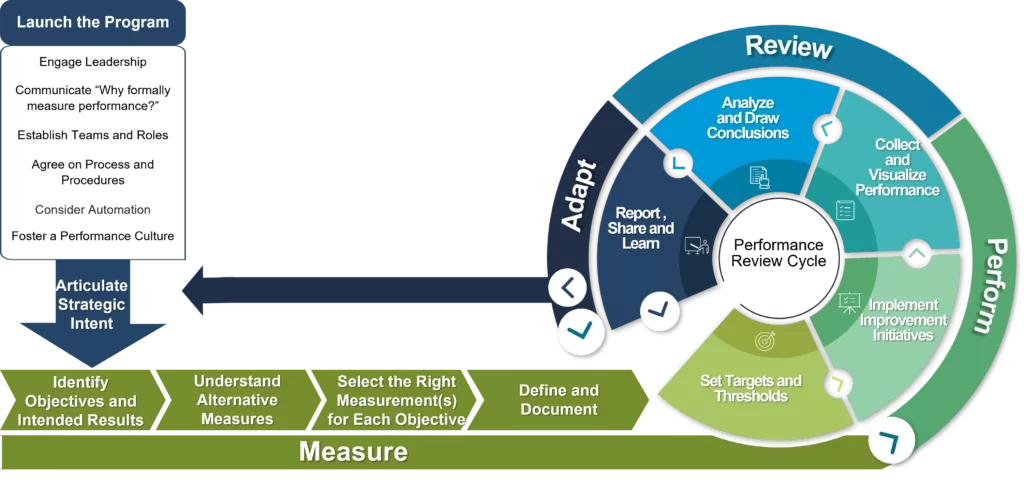
"The Balanced Scorecard Institute’s (BSI) Measure-Perform-Review-Adapt (MPRA) framework is a disciplined, practical, and tested approach for developing and implementing a KPI system. It gives organizations a way to systematically articulate a shared vision of what you are trying to achieve, set practical goals, develop meaningful indicators that can be managed and used for decision-making, and establish long-term discipline around getting things done."
Step One: Launch the Program
KPIs require an initiative (i.e.a product, service or experience) and so in order to do this, there must be a clear understanding of what is going to be done, by who and the strategic intent (i.e. the why).
During this process you may:
- Interview key stakeholders.
- Engage with the client or leadership.
- Establish "why you are measuring performance."
- Establish the expected outcome.
- Establish the team(s) and roles.
- Agree on process and procedures.
Step Two: Measure
The measure phase is intended to cover the steps outlined below with the purpose of ensuring that the right KPIs are assigned to the initiative.
Identify Objectives and Intended Results
The development of meaningful KPIs starts with understanding the strategic intent in order to find the right objectives and outcomes.
Understand Alternative Measures
Once you understand the objective and expected result, you need to identify if they are analytically measurable.
If they cannot be measured directly, you may need to define indirect measures that result in a measurable result.
For example, if the objective is to deliver on time, the KPIs might be to have a strong process that can be measured periodically (i.e. sprints) and therefore serves as a better continuous measure as well as to ensure that you do not lose team members on the way.
Select the Right Measure(s) for Each Objective
The best KPIs are those that are concise and concrete. Reduce the number of KPIs identified to those that are most important and relevant.
KPI.org's suggested framework for this is to ask yourself if the KPIs:
- Have meaning and relevance.
- Answer key user questions about the organization’s performance towards strategic objectives.
- Provide information needed to make better strategic decisions.
- Are valid and verified, measuring what is intended.
- Encourage desirable employee behaviors.
- Avoid an undue data collection burden or unintended consequences.
Define and Document Selected Performance Measures
Document the KPIs and how you intend to measure them, review them and potentially adapt them over time.
Step Three: Perform
Performance review cycle follows a regular pattern around a simple pattern: set targets, implement improvement actions, track performance and learn from the results.
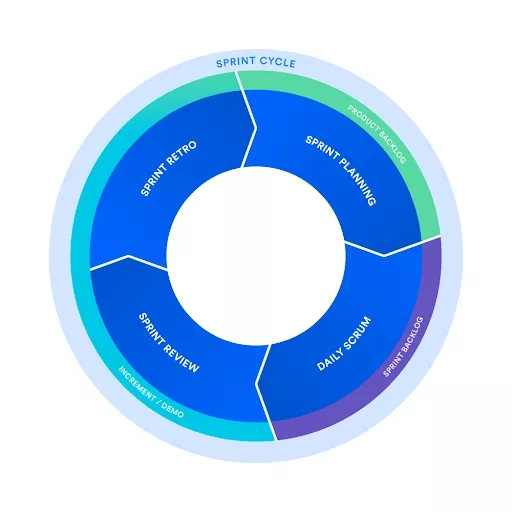
Although KPI.org suggests that you do this quarterly, we recommend that you implement scrum and do this on a bi-weekly cadence with daily stand-ups.
Step Four: Review
In the Review phase of the process, data is transformed into evidence-based knowledge and understanding. The Review phase is organized around two process component steps: 1. collect and visualize performance and 2. analyze and draw conclusions.
We recommend that you do this using sprint reviews, burndown charts and sprint retrospectives.
Step Five: Adapt
The Adapt phase of the process explores whether improvement strategies were effective and correctly executed, and if assumptions turned out to be valid. It includes an periodic assessment of performance results (i.e. quarterly or bi-weekly), which can lead to a re-forecasting of performance targets, a new set of actions or initiatives, or a complete recalibration of strategy, as needed.
Sometimes the Adapt phase leads to the continuation of current activities and sometimes it means refocusing Strategic Intent based on a changing strategic environment. This phase focuses on identifying what worked well and what didn’t, taking corrective action and becoming a high-performance organization.
To make sure that your objective is consistently prioritized and that your initiative is up to date we recommend that you implement a product roadmap, backlog and update it constantly through backlog grooming.
Looking to learn more about Project Management, Technology and Strategy?
Search our blog to find educational content on project management, design, development and strategy.