What is Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs?
Abraham Maslow (1954) created a five (5) tier pyramid that describes the order in which humans seek to full-fill needs in order to feel motivated to act and evolve.

Abraham Maslow (1954) created a five (5) tier pyramid that describes the order in which humans seek to full-fill needs in order to feel motivated to act and evolve.
SubscribeConsult McLeod, S. A. (2018, May 21). Maslow's hierarchy of needs.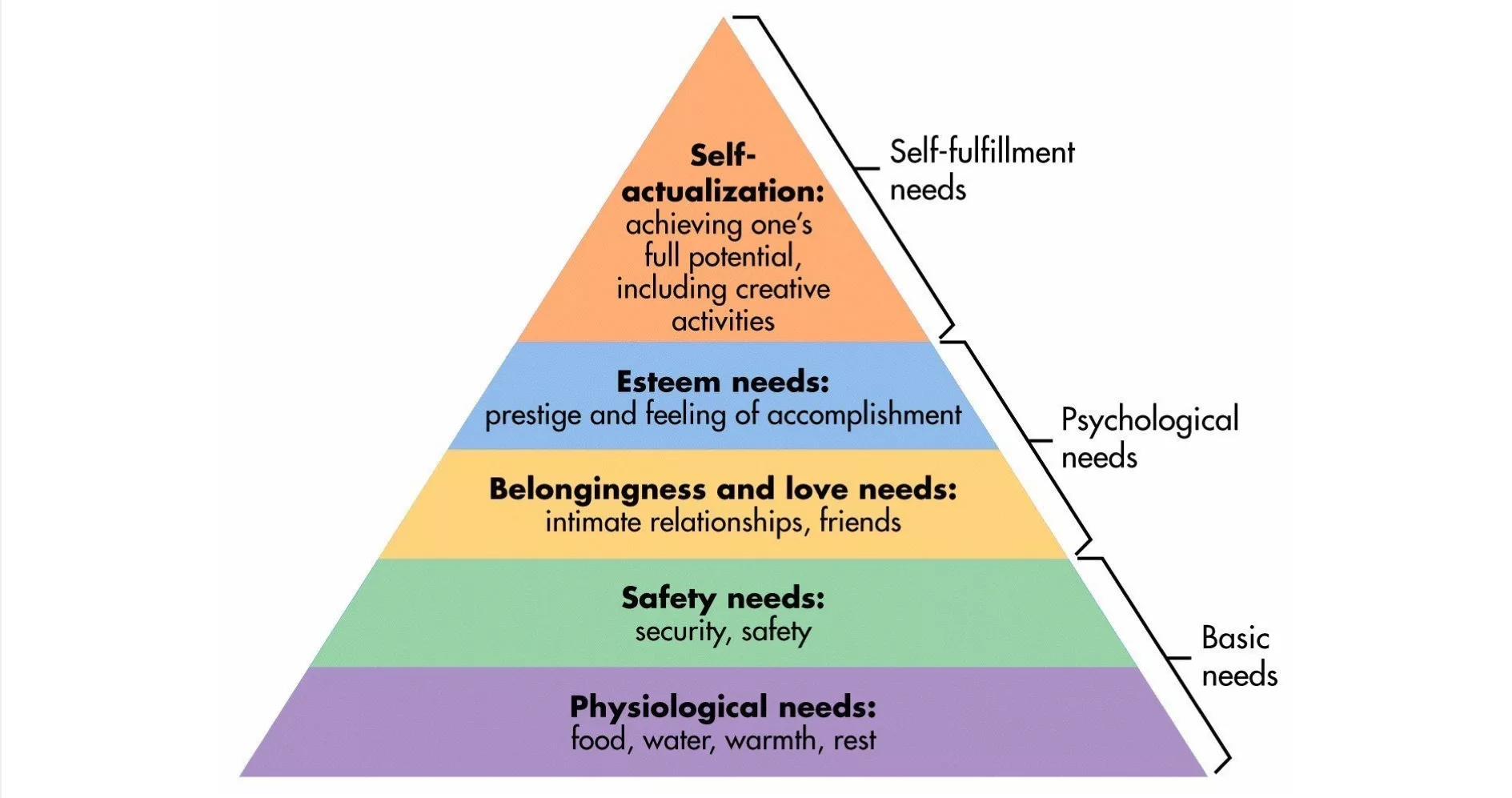
Maslow's original five-tier (5) pyramid.
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs is a motivational psychological theory that is compromised of 5 levels:
- Psysiological needs: Food, water, warmth, rest, sex, sleep.
- Safety: Security, safety, order, law and stability.
- Love and Belonging: Intimate relationships, friends, trust, acceptance, receiving, giving and being a part of a group.
- Self-esteem: Prestige, feeling of accomplishment, dignity, desire for respect and reputation.
- Self-actualization: Achieving one's full potential, including creative activities, self-fulfillment, seeking personal growth and peak experiences.
Maslow dictated that the lower needs (i.e. physiological needs) need to be fulfilled in order for humans to be able to attend to higher needs (i.e. safety) and that ultimately, humans just wanted to self-actualize but could only do so once everything else was met.
Please note that Maslow believed that needs do not need to be fulfilled 100% for an individual to move onto the next tier.
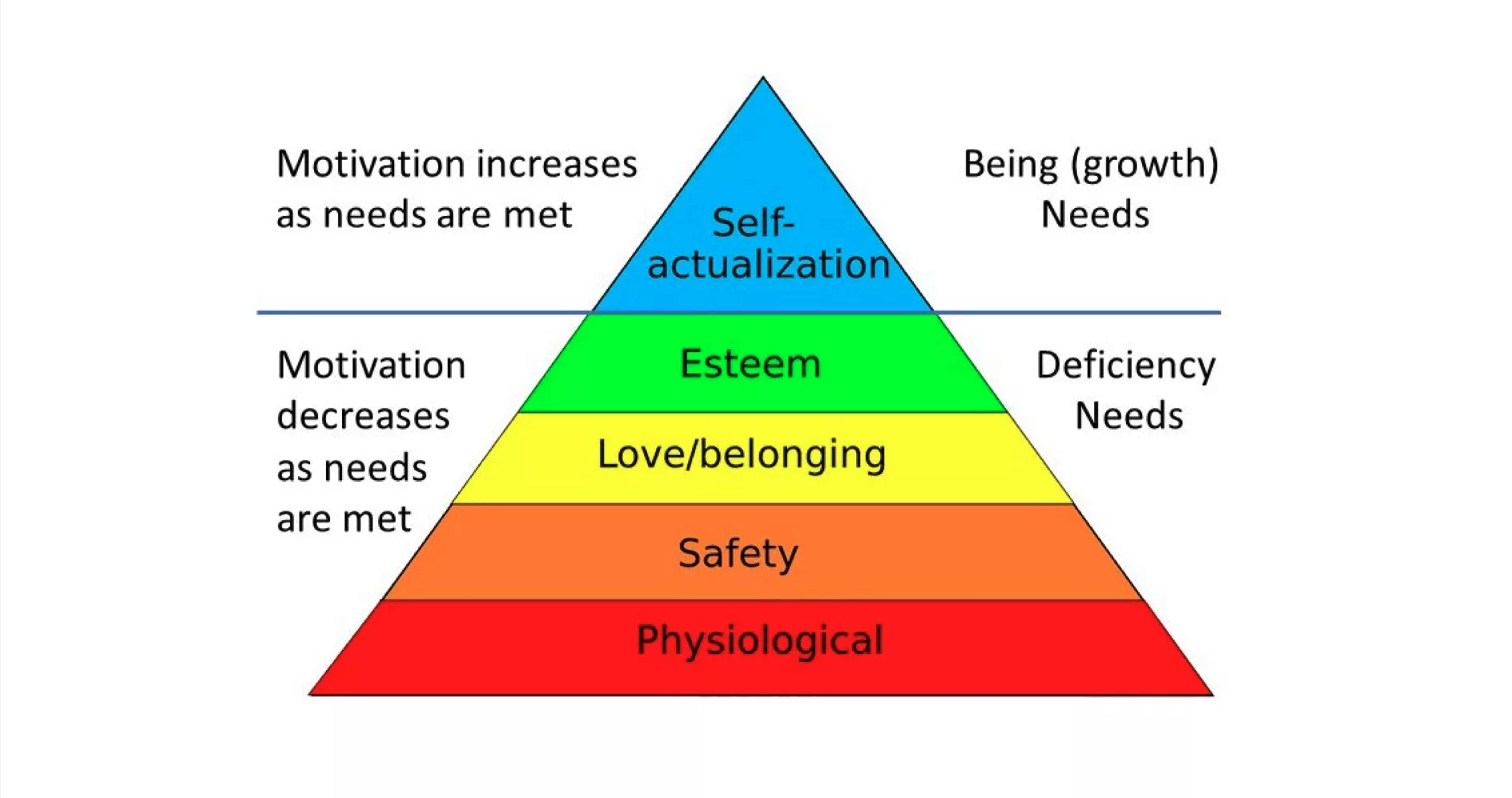
Maslow's original five-tier (5) pyramid divided into Deficiency & Growth.
Leading researchers believe that this pyramid can be split into two parts growth and deficiencies.
For deficiencies (physiological, safety, love and belonging and self-esteem), as the needs are met, individuals are less motivated to fulfill them.
On the other hand, for growth (i.e. self-actualization), the more an individual self-actualizes, the more motivated they feel to self-actualize.
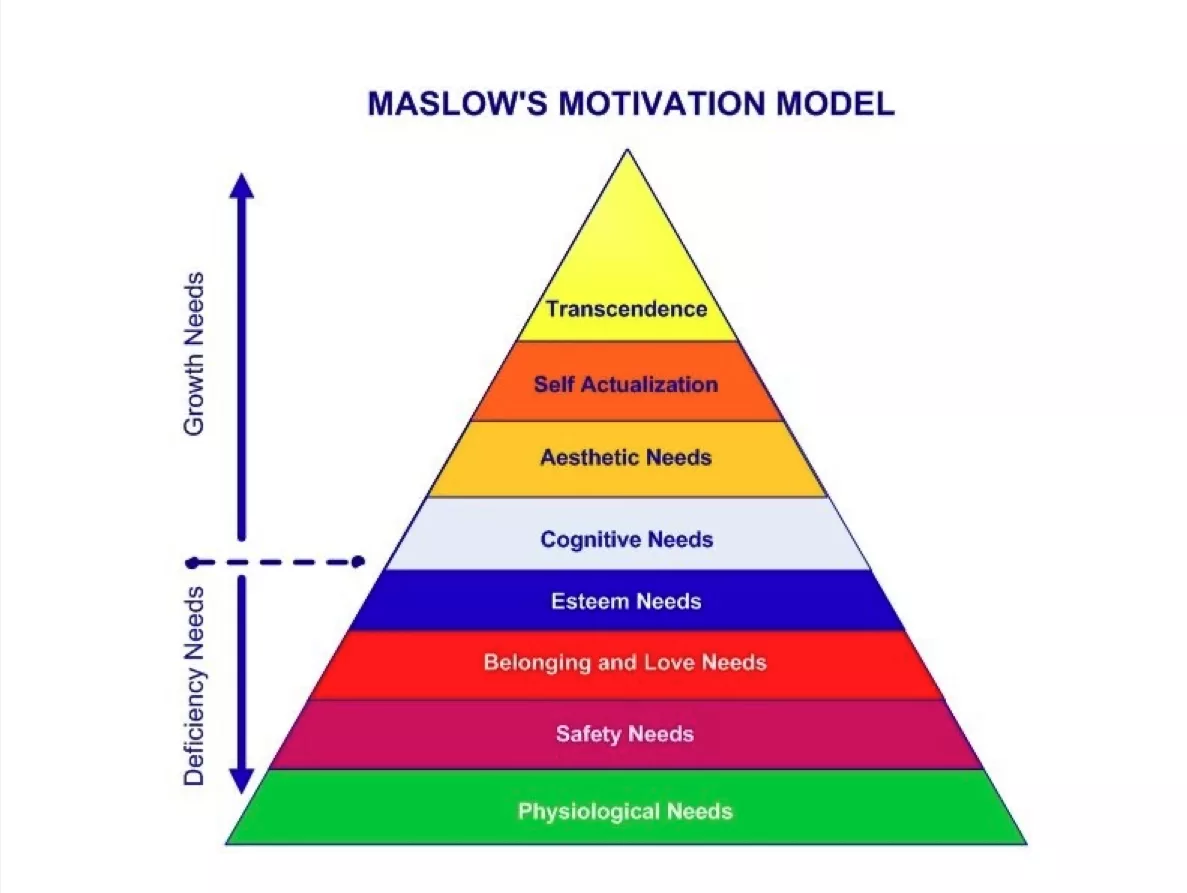
Maslow's updated eight-tier (8) pyramid divided into Deficiency & Growth.
Recently, Maslow's original five(5) tier model has been expanded to include the cognitive and aesthetic needs (Motivation and personality, 1970) and transcendence needs (Religions, values, and peak experiences, 1970) converting the pyramid into a eight(8) tier model.
These new tiers can be described as:
- Cognitive: Knowledge and understanding, curiosity, exploration, need for meaning and predictability.
- Aesthetic: Appreciation and search for beauty, balance and form.
- Transcendence: A person is motivated by values which transcend the personal self (e.g., mystical experiences and certain experiences with nature, aesthetic experiences, sexual experiences, service to others, the pursuit of science, religious faith, etc.).
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs & Innovation
When carrying out user research to develop a new product, service or experience (i.e. an initiative) for a target audience, we recommend that companies and individuals integrate Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs into the user persona, empathy map or value proposition canvas in order to gain a more in-depth understanding of who it is that you are creating for.
They are also vital in the creation of a new brand, by applying it to a brand pyramid.
We believe that by doing so, companies and individuals will be able to differentiate themselves and produce greater value, resulting in a return on investment.
Looking to learn more about Innovation, Project Management, Design, Technology and Strategy?
Search our blog to find educational content on innovation, project management, design, development and strategy.