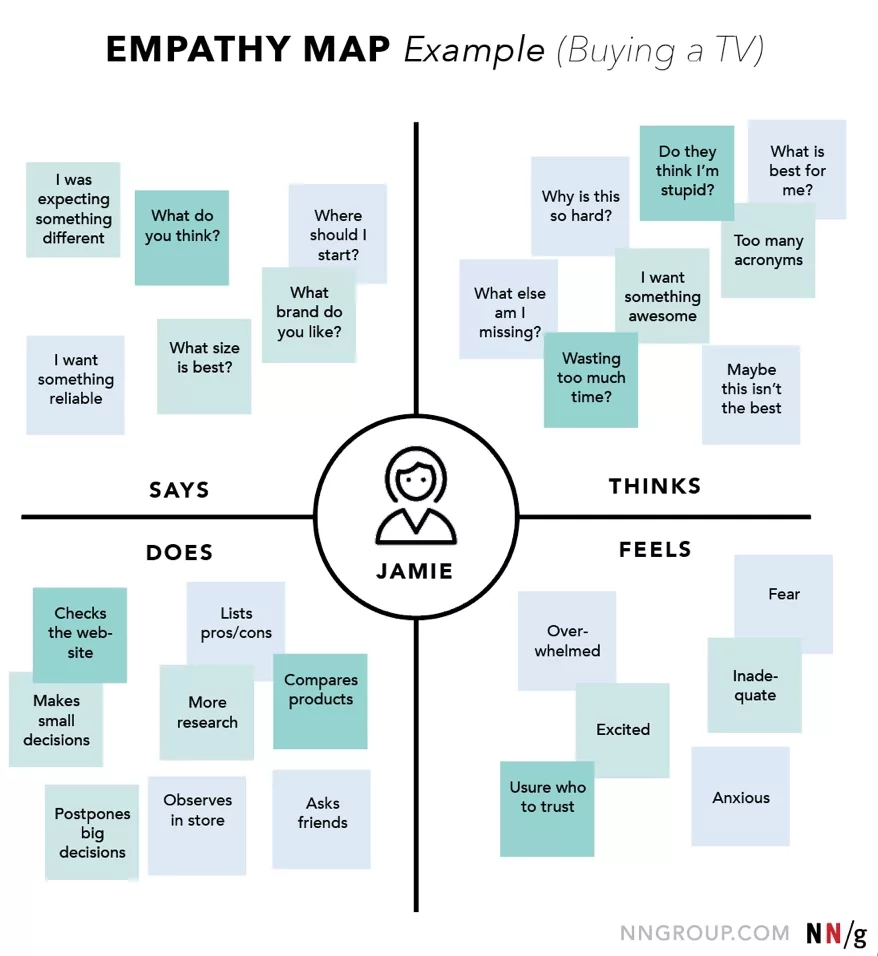
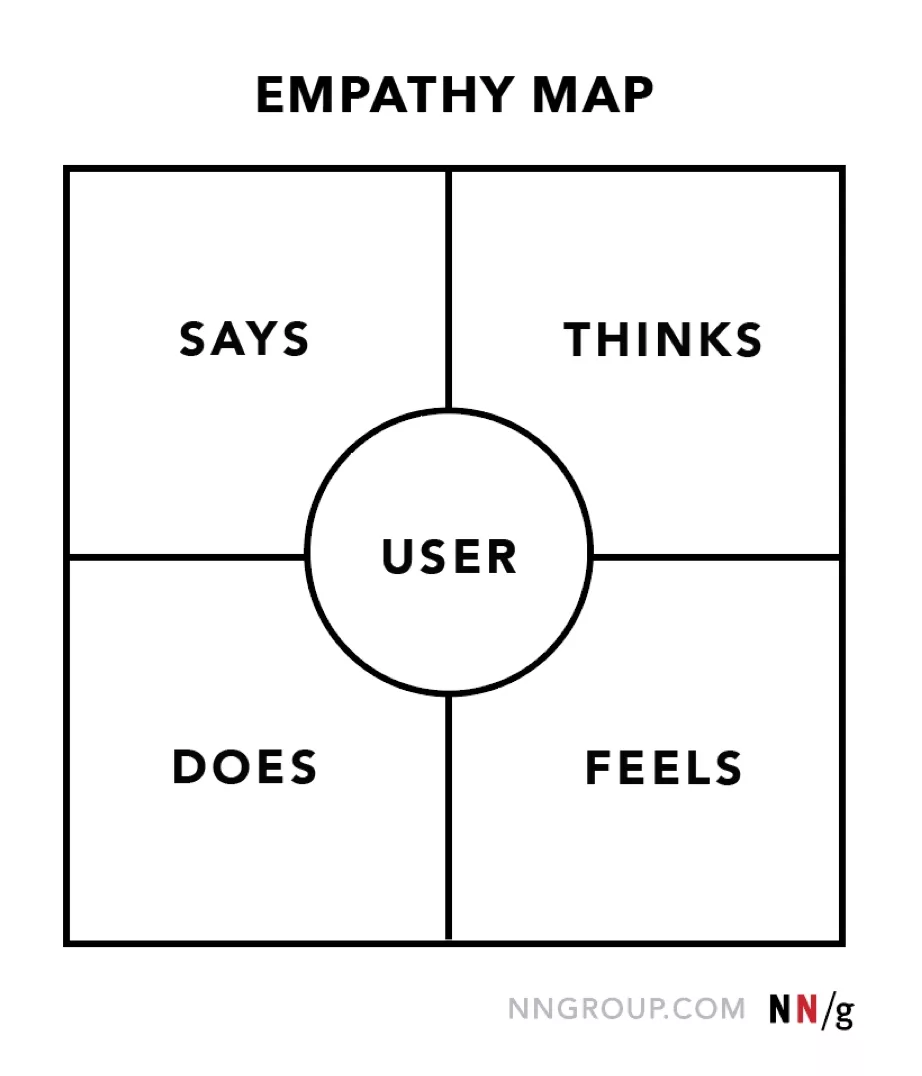
What is an Empathy Map?
A holistic visualization of a user's attitudes and behaviors towards a product, service or experience.

A holistic visualization of a user's attitudes and behaviors towards a product, service or experience.
SubscribeWhen creating a product, service or experience (i.e. a creation) it is fundamental that we understand who we are creating for (i.e. the target audience) and how to create something that provides value to them in a way that results in a return on investment.
As part of this process, individuals and organizations often carry out user research, desk research and interviews as a means of better understanding the target audience.
A synthesized product that often comes out of this research is an empathy map, which is a design thinking methodology and a design research tool that visualizes and describes how a persona feels as they think, discuss or uses a creation.
Empathy maps can come in handy when designing journey maps or service blueprints.
Empathy maps help organizations or individuals onboard employees on:
- How users feel about their creation.
- Serve as a centralized point of reference how users feel.
- Serve as a mirror to help organizations make informed, sound and thoughtful decisions.
What makes up an Empathy Map ?
An empathy map consists of four quadrants: Says, Thinks, Does and Feels and are meant to be analyzed and used in a way that is neither sequential or chronological.
At the center of the quadrant should sit the persona of the user.
Says
The Says quadrant shows what a user says in an interview or a usability test and should be written verbatim.
Thinks
The Thinks quadrant occupies what the user thinks about during the entire process.
Questions that you could ask yourself to populate this quadrant include:
- What are the users thoughts?
- What matters to the user?
Please note that it is possible to have the same content in Thinks and Says, in the even that the user said that they think about certain things during interviews or tests.
Does
The Does quadrant encloses the actions of the user takes.
This is our suggested quadrant for including the jobs that a user does in relation to the creation. These jobs may reveal gaps in the market that could be fulfilled by your business as a means to enhancing the lives of the user.
To learn more consult the Harvard Business School article linked below.
Feels
The Feels quadrant should reflect the users emotional state.
Questions that you could ask yourself to populate this quadrant include:
- What worries the user?
- What does the user get excited about?
- How does the user feel about the creation?
- Where does the user get disappointed?
Want to learn how to create Empathy Maps?
To learn our approach to creating empathy maps, consult the link below.
Looking to learn more about Research and Strategy?
Search our blog to find educational content on research and strategy.