How to create and use environment variables in Typescript & Serverless
A step by step guide on adding environment variables to a Typescript & Serverless project through its serverless.yml and using them within a function.
A step by step guide on adding environment variables to a Typescript & Serverless project through its serverless.yml and using them within a function.
The following tutorial makes use of our Typescript & Serverless Starter project and walks you through how to create and use environment variables. To learn more about environment variables in Serverless or how we created the Typescript Serverless starter project please use the links below.
We recommend downloading our Open Source project, checking out the main branch and carrying out the steps outlined below. All relevant changes can be found on the tutorial/environment-variables branch.
git clone git@github.com:delasign/typescript-serverless-starter.gitStep One: Add the environment variable
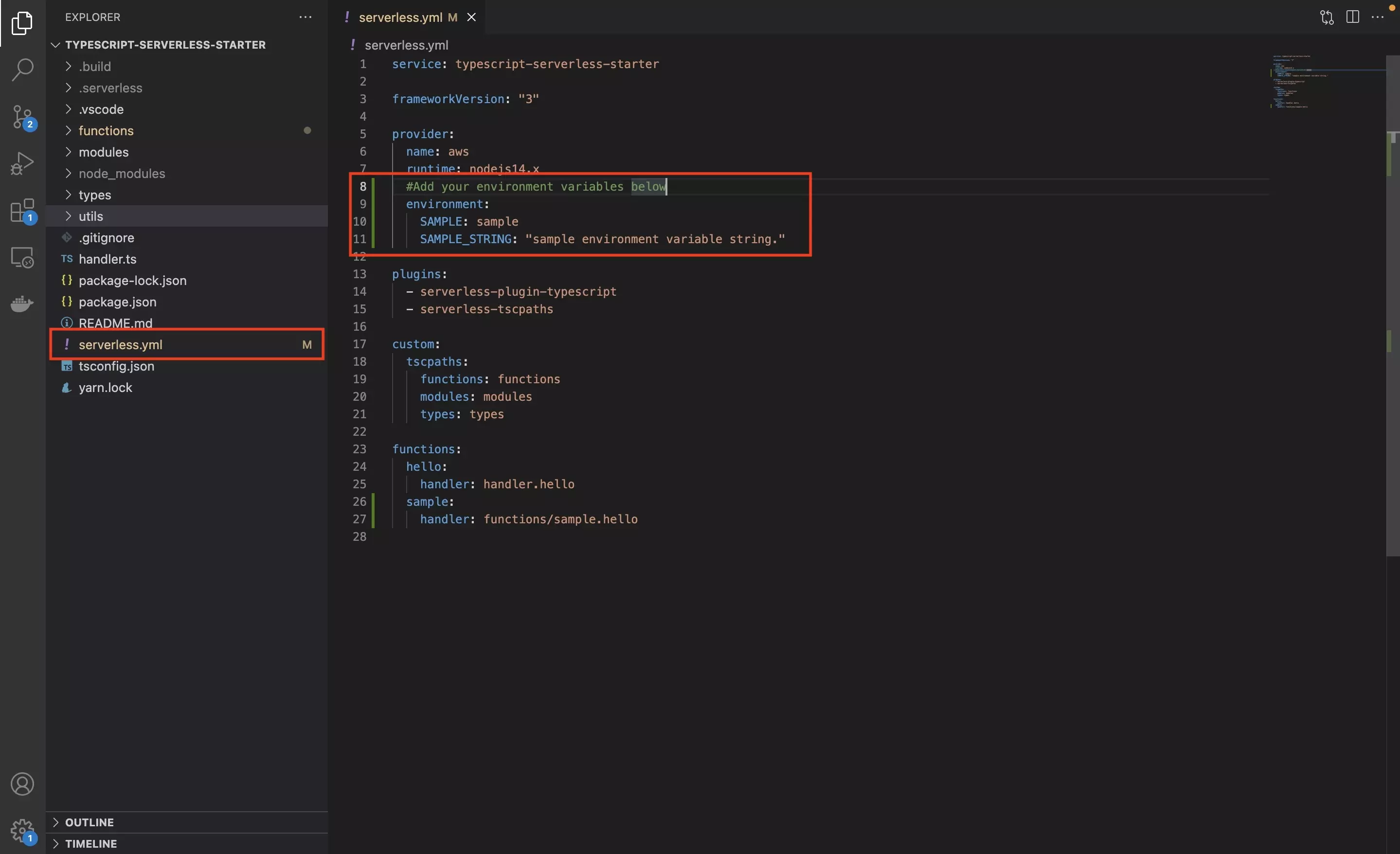
In the serverless.yml under the provider, add an indentation and add a new parameter called environment.
Within the environment parameter, add your environment variables as shown below.
Step Two: Use an environment variable in a function
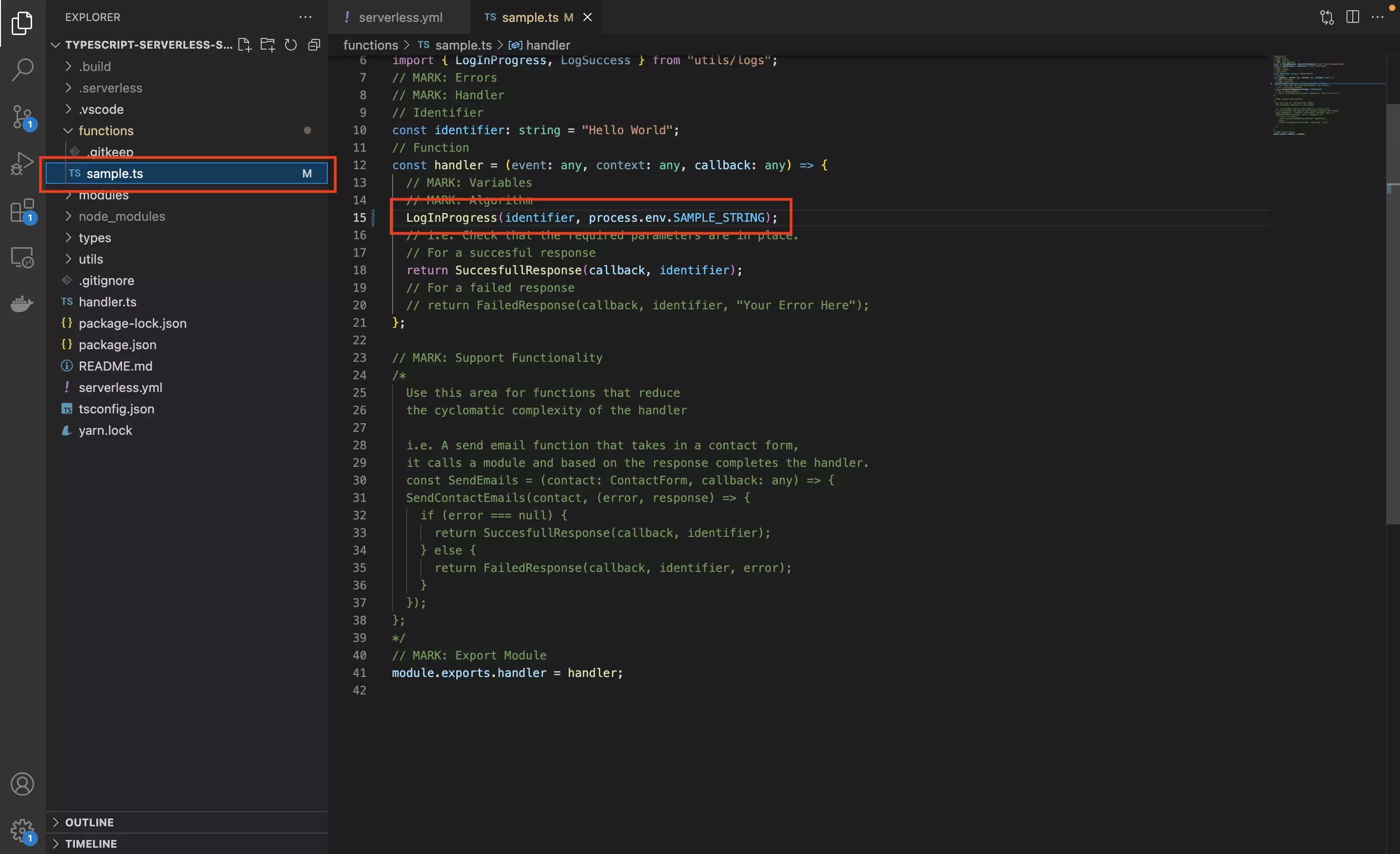
To use an environment variable in a function you must use the following notation, where ENV_NAME is the name of your environment variable declared in your serverless.yaml.
process.env.ENV_NAMEIn the sample code below, we have modified the Serverless function found at functions/sample.ts and have used our log system to log the environment variable for the purposes of confirming that our methodology works.
Step Three: Test
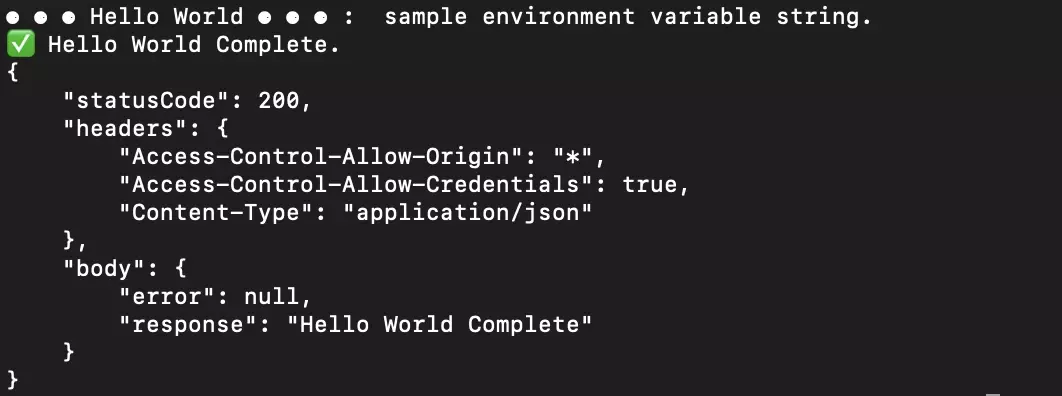
In Terminal, invoke your function locally to test that the environment variable registered in the function.
Step Four: Use an environment variable in the serverless.yml
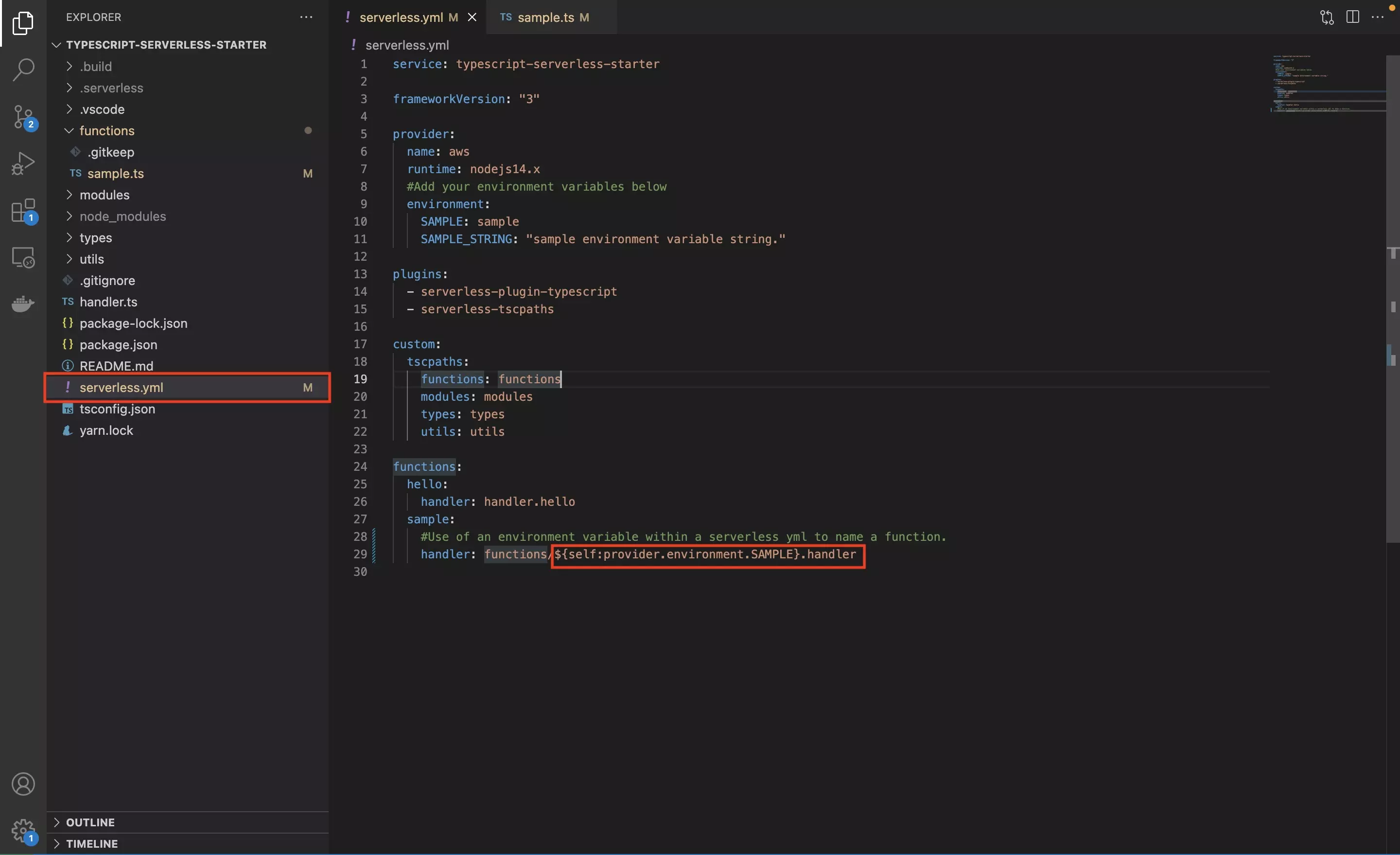
To use an environment variable in the serverless.yml you must use the following notation, where ENV_NAME is the name of your environment variable declared in your serverless.yaml.
${self:provider.environment.ENV_NAME}In the sample code below, we have replace the sample with the sample environment variable, to demonstrate that you can use an environment variable to give name to a function.
Step Five: Test

In Terminal, invoke your function locally to test that the environment variable registered in the serverless.yml.
Any Questions?
We are actively looking for feedback on how to improve this resource. Please send us a note to inquiries@delasign.com with any thoughts or feedback you may have.