How to push branches to a git remote using Terminal
A step by step guide on pushing all your branches to new git remote using Terminal.
Written by Oscar de la Hera Gomez
First published on 06/04/2023 at 15:47
Last Updated on 06/04/2023 at 17:02
A step by step guide on pushing all your branches to new git remote using Terminal.
SubscribeStep One: Set the current directory
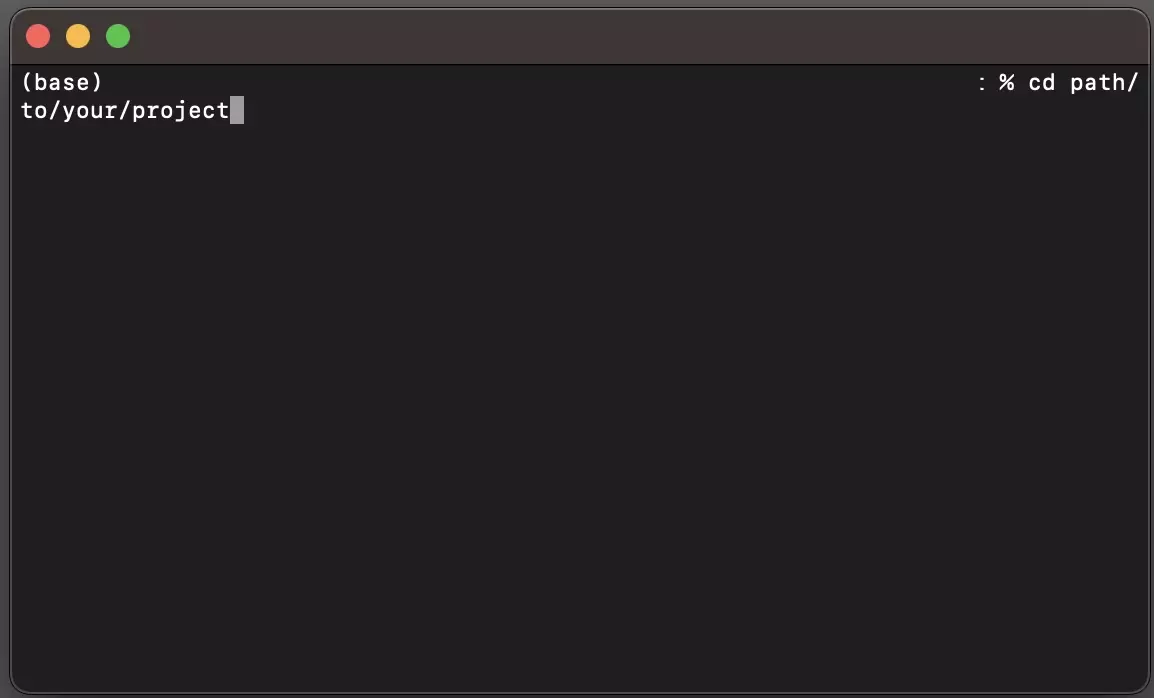
Open Terminal, and set the current directory to that of your project using a command similar to the one below.
cd path/to/your/projectStep Two: Get all branches
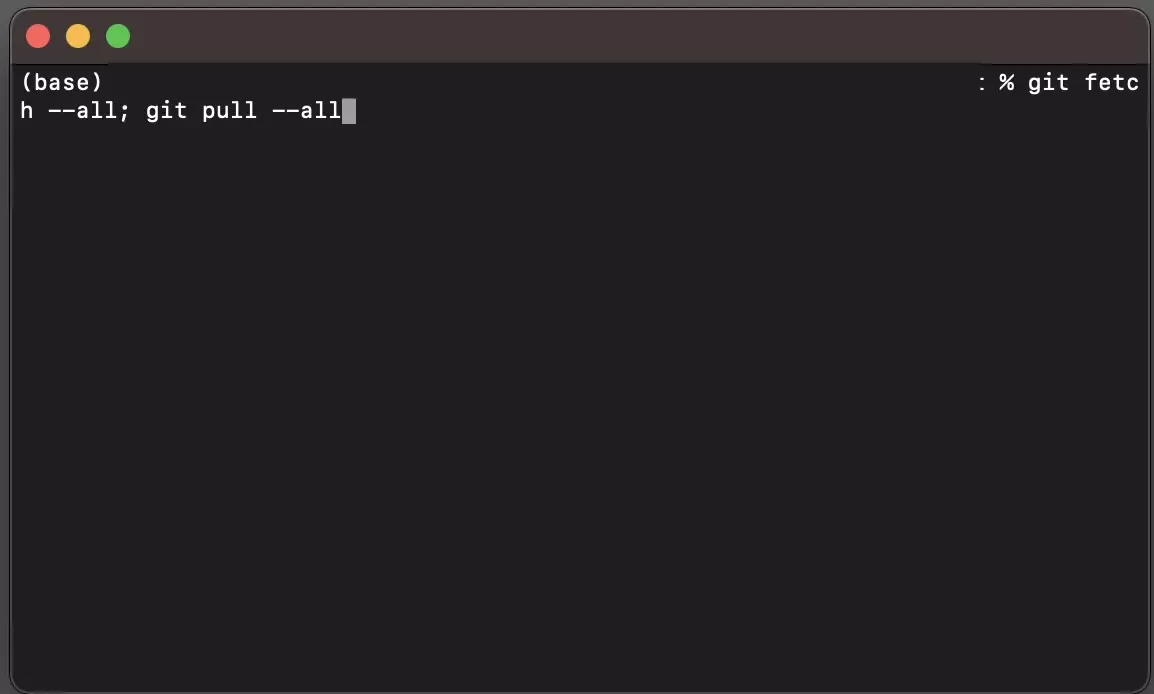
Run the following line in Terminal to fetch and pull all the branches
git fetch --all; git pull --allStep Three: Push all the branches to remote
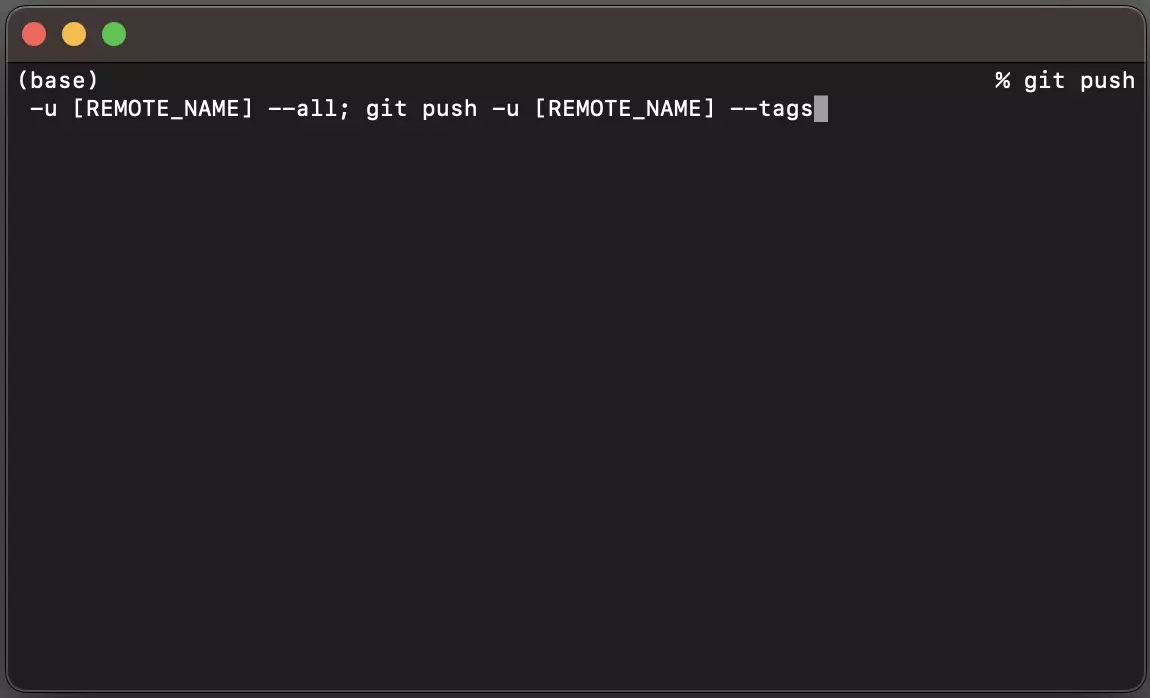
Push all the branches to your new remote by running the line below in Terminal.
git push -u [REMOTE_NAME] --all; git push -u [REMOTE_NAME] --tagsPlease ensure that you replace REMOTE_NAME with the name of your Git remote.
Any Questions?
We are actively looking for feedback on how to improve this resource. Please send us a note to inquiries@delasign.com with any thoughts or feedback you may have.
SubscribeContact UsVisit our BlogView our ServicesView our Work