How to maintain state values when Android changes configuration
A step by step guide on keeping state values within an Activity during configuration changes such as a change in screen orientation, language or input devices.
A step by step guide on keeping state values within an Activity during configuration changes such as a change in screen orientation, language or input devices.
SubscribeDownload Open Source Kotlin Starter ProjectWhat is happening ?
"If the configuration of the device (as defined by the Resources.Configuration class) changes, then anything displaying a user interface will need to update to match that configuration. Because Activity is the primary mechanism for interacting with the user, it includes special support for handling configuration changes.
Unless you specify otherwise, a configuration change (such as a change in screen orientation, language, input devices, etc) will cause your current activity to be destroyed, going through the normal activity lifecycle process of onPause(), onStop(), and onDestroy() as appropriate. If the activity had been in the foreground or visible to the user, once onDestroy() is called in that instance then a new instance of the activity will be created, with whatever savedInstanceState the previous instance had generated from onSaveInstanceState(Bundle)."
Tutorial
The following tutorial demonstrates how to maintain the experience state state value of the MainActivity in our Open Source project. This makes sure that the app shows the user the same screen as they were on after an orientation change.
If you wish to test it, download the project through the repository linked below.
Step One: Create the Key(s)
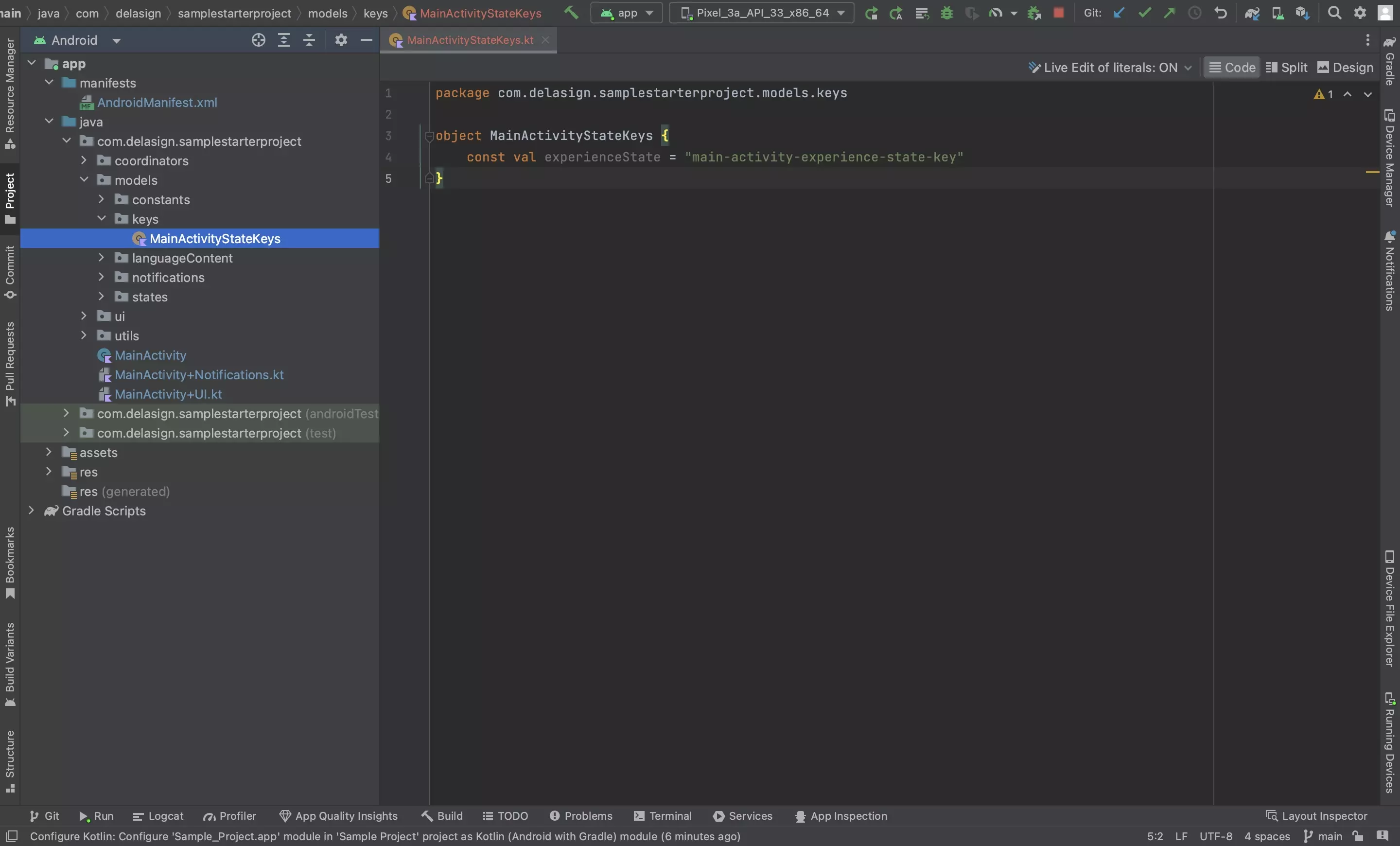
We recommend creating a file per activity in your project and creating a string that serves as a type-checked constant for saving and retrieving states.
Step Two: Save the State(s)
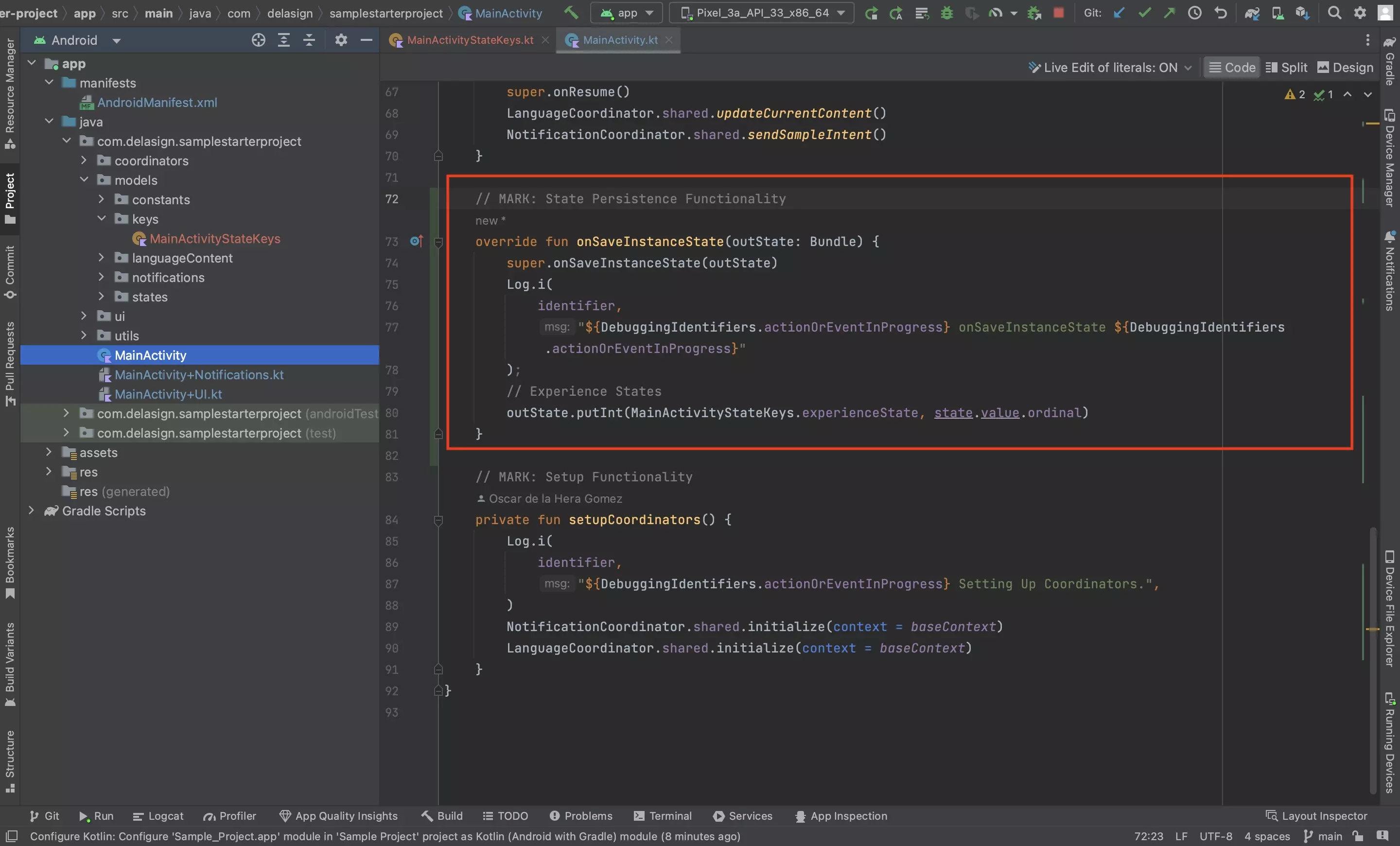
In the relevant activity, save the state(s) using the key(s) created in Step One.
Step Three: Restore the State(s)
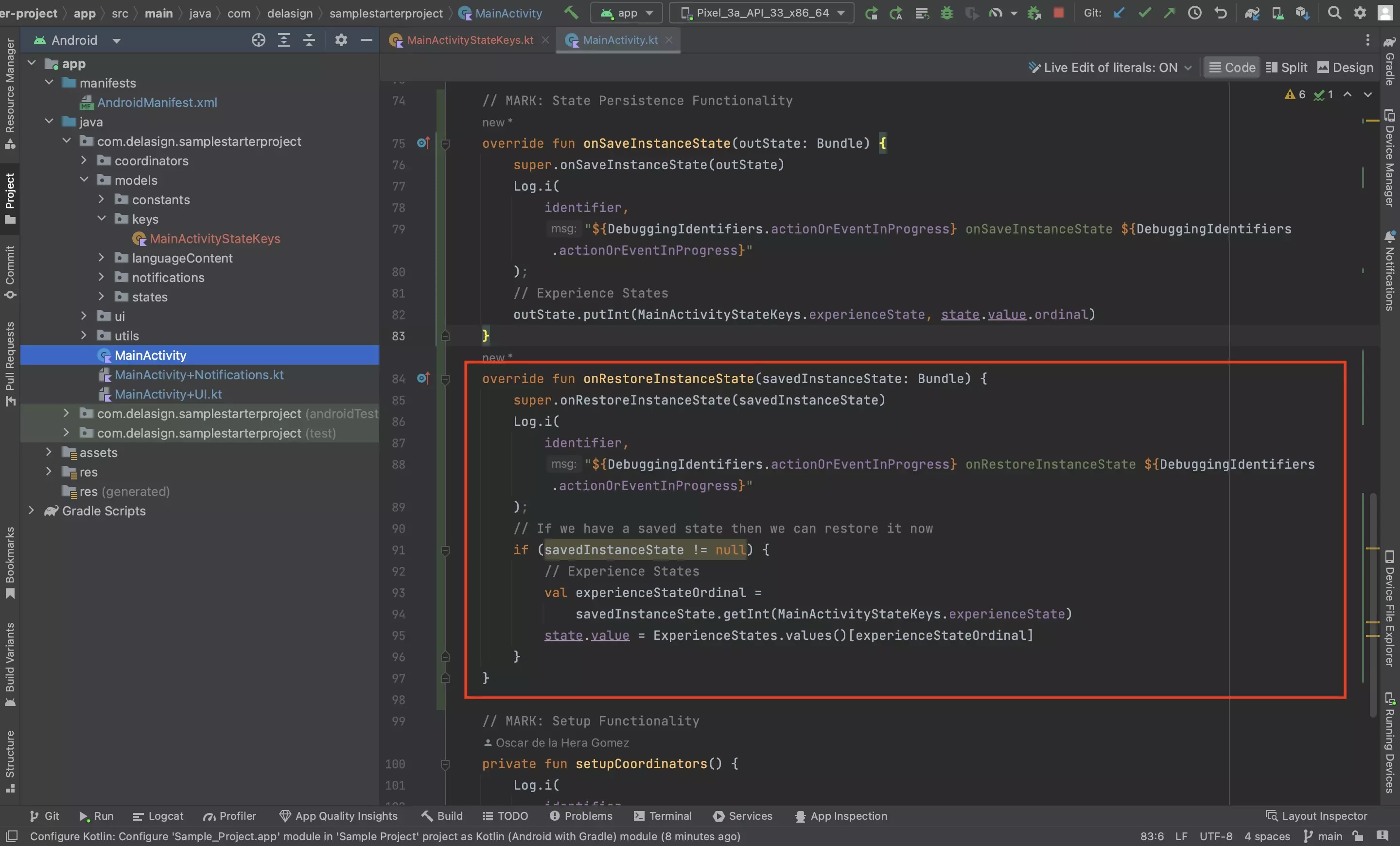
In the same activity, restore the state(s) using the key(s) created in Step One.
Step Four: Test
Run the app and confirm that the states persist when the Android configuration changes.