How to create an Android Notification Coordinator in Kotlin
A step by step guide on creating a manager that can send intents from any activity or composable which can be received across an Android app.
A step by step guide on creating a manager that can send intents from any activity or composable which can be received across an Android app.
SubscribeDownload Open Source Kotlin Starter ProjectThis post is the first part of a mini series on sending and receiving functional intents in an Android app. The rest of the tutorials are available at the end.
Please note that we have chosen to use the term "Notifications" to standardize naming conventions across iOS and Android. If you wish to exchange Notifications for Intents, we welcome you to.
Step One: Create the Package
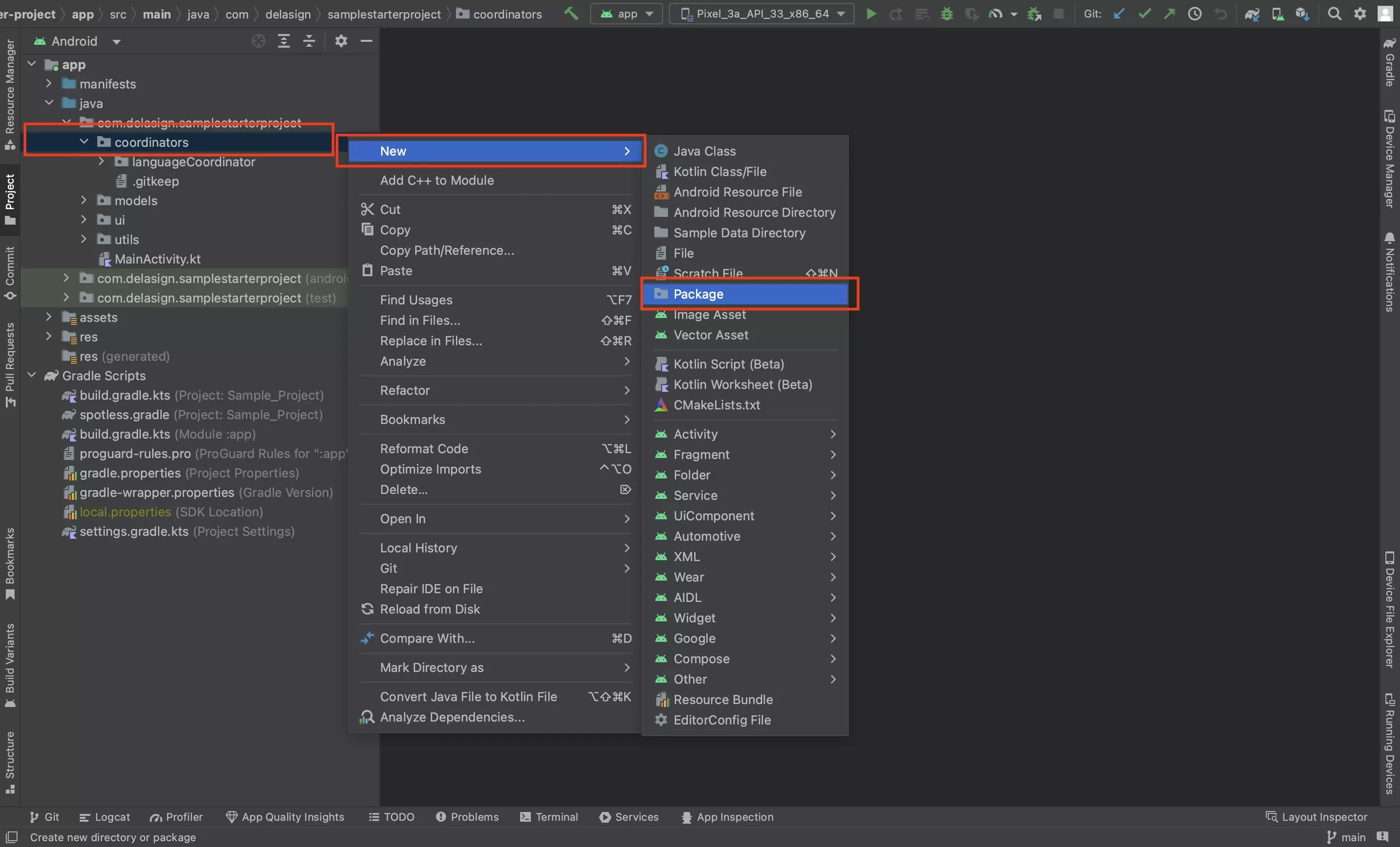
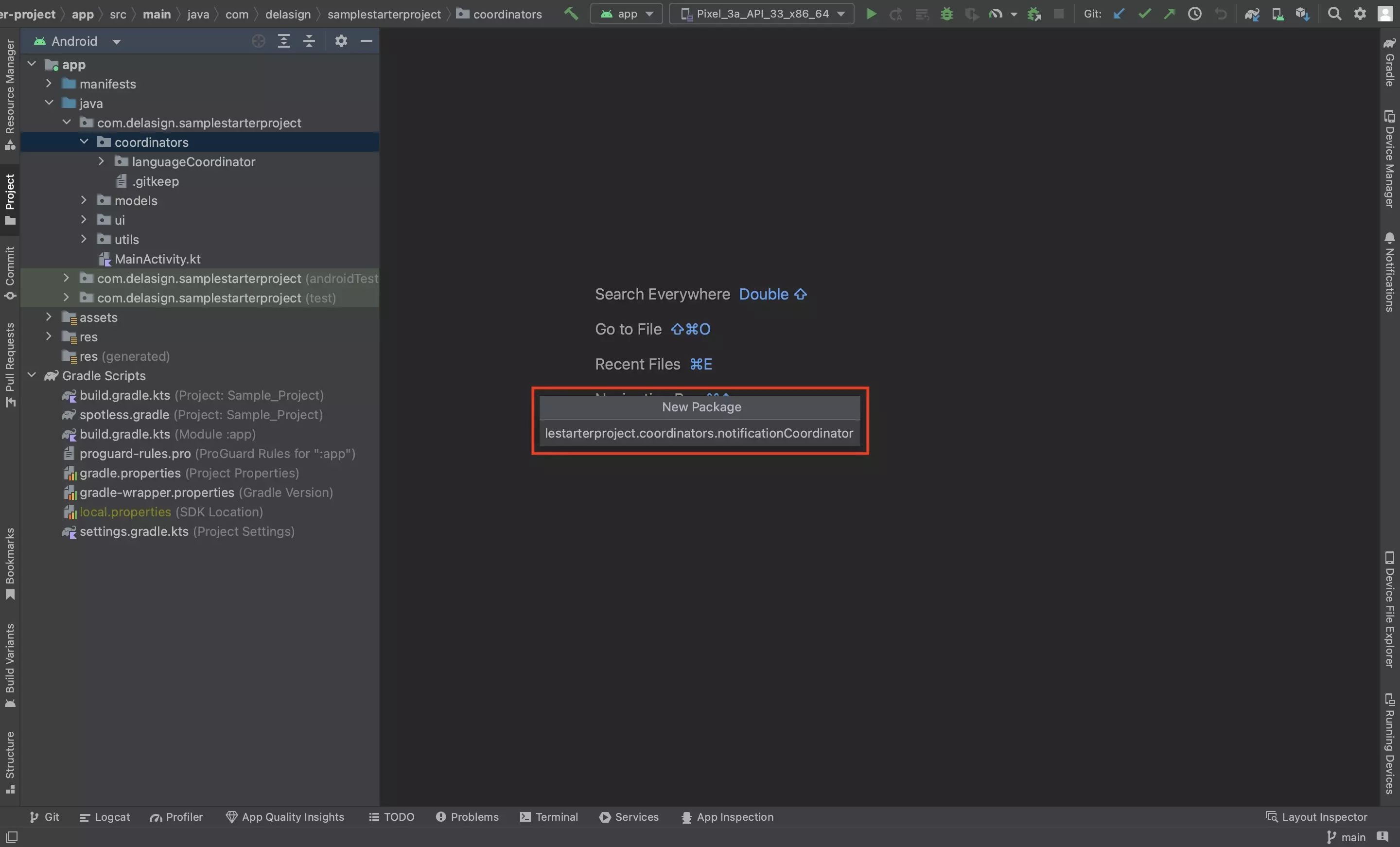
In the project, create a package called notificationCoordinator.
We recommend that you place it under coordinators.
Step Two: Create declaration file
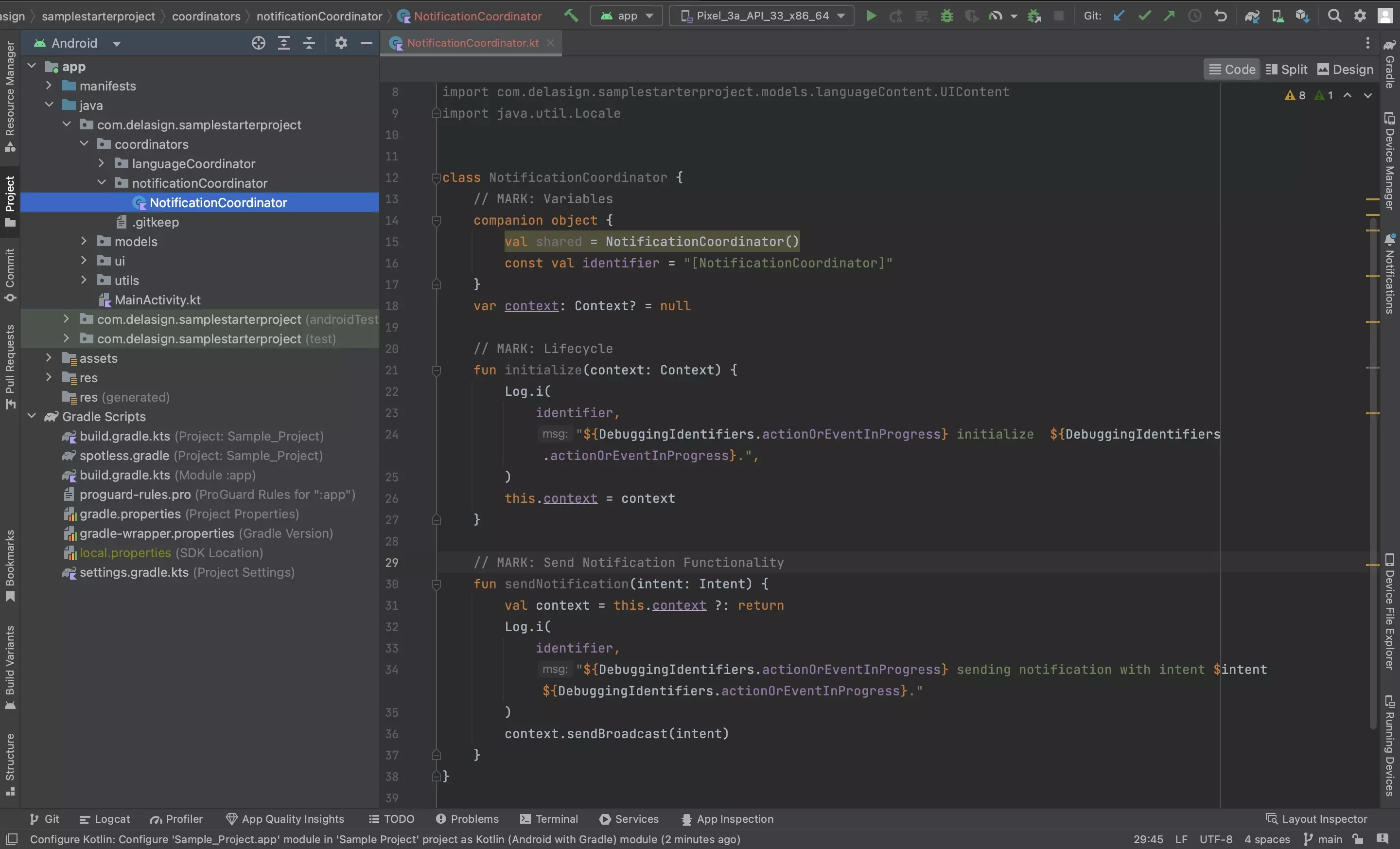
In the package created in Step One, create a new Kotlin file called NotificationCoordinator.kt and paste in the code below.
Step Three: Create the Internal Intents Extension
In the package created in Step One, create a new Kotlin file called NotificationCoordinator+InternalIntents.kt and leave it blank for now.
This is where you will add functionality to standardize how you send intents within your application that are only available to your application.
Step Four: Create the External Intents Extension
In the package created in Step One, create a new Kotlin file called NotificationCoordinator+ExternalIntents.kt and leave it blank for now.
This is where you will add functionality to standardize how you send intents within your application that are available outside of your application.
Step Five: Initialize
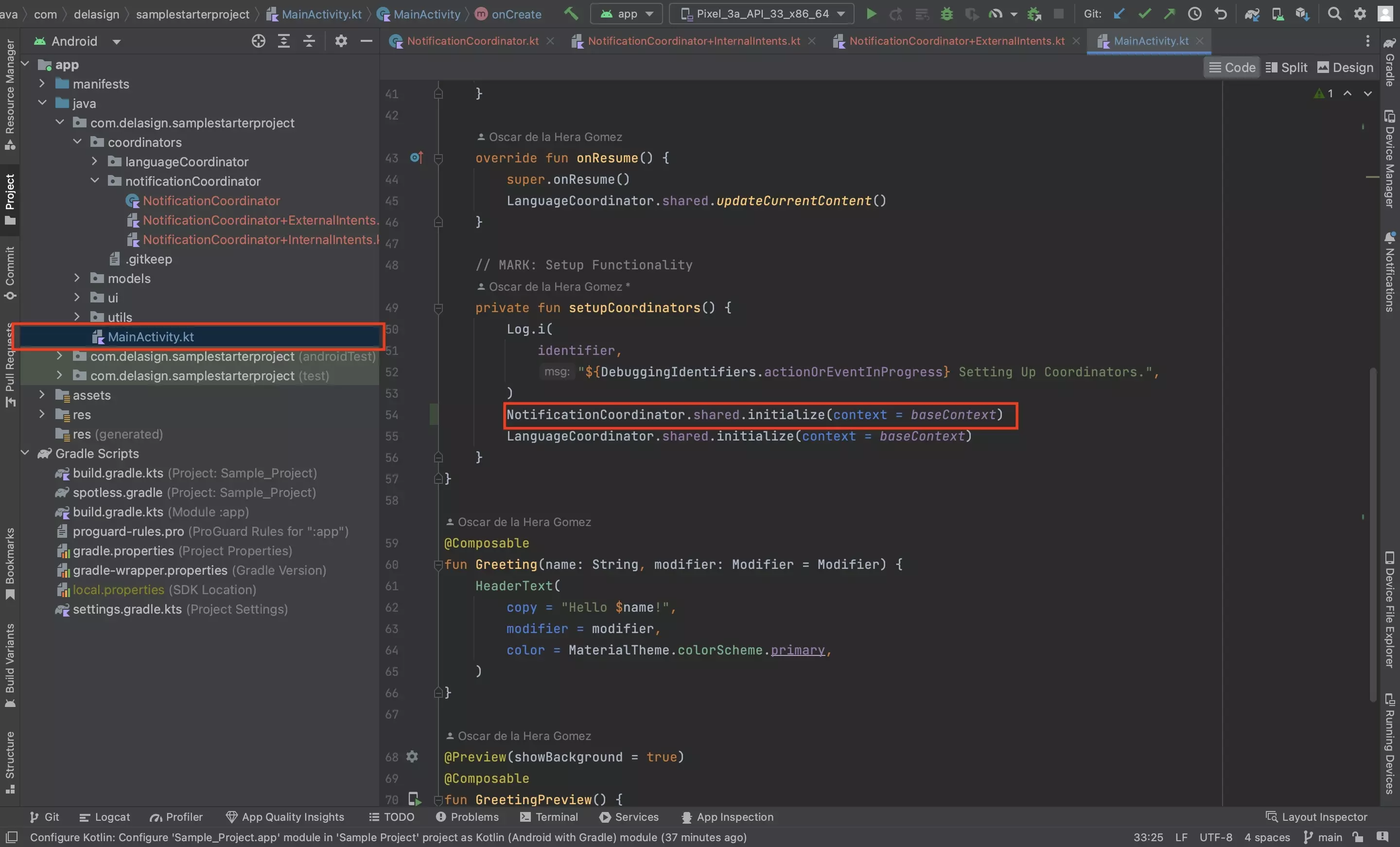
The coordinator requires the base context to be able to provide receivable notifications to an app.
Initialize the NotificationCoordinator in your MainActivity.kt using the function below.
We recommend that you do this in a function called setupCoordinators() which is initialized onCreate.
NotificationCoordinator.shared.initialize(context = baseContext)Looking to learn more about Intents in Android ?
Consult the tutorials linked below to learn more about sending and receiving Intents in Android and Kotlin.